Ankle
Accessory Muscle of Ankle
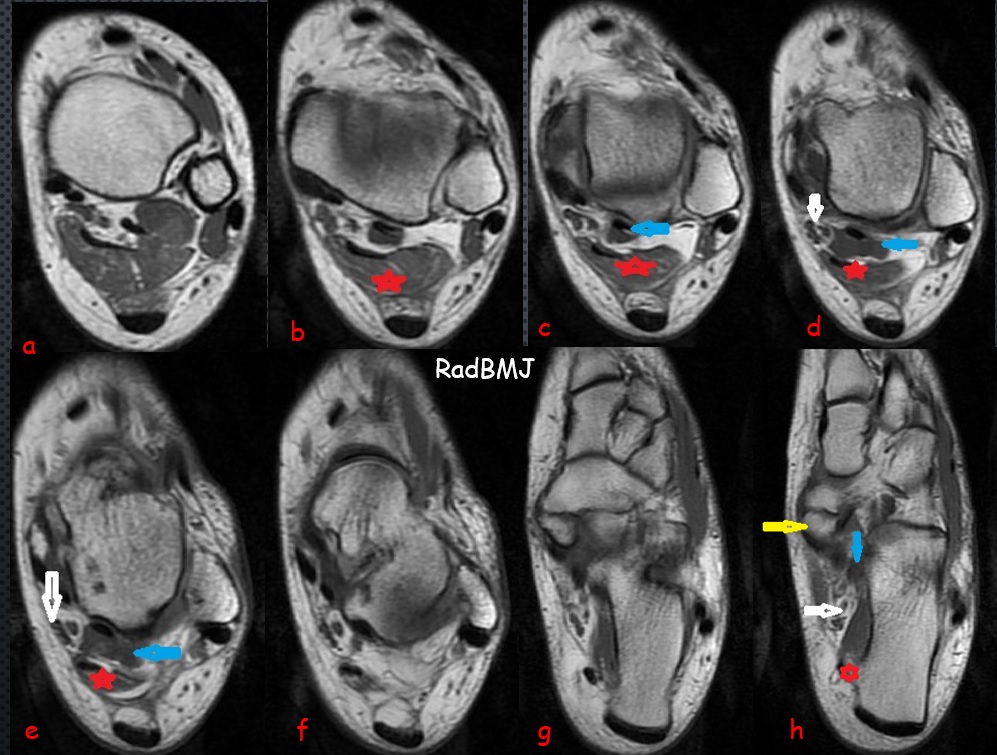
Image Detail: Sequential Axial plane T1W images demonstrates a triangular shaped accessory muscle (red star) abuts the adjacent neurovascular bundle (white arrow) and lies posterior-medial to the FHL muscle (blue arrow). There is also type 2 accessory navicular bone articulating with medial part of navicular bone (Yellow arrow). Accessory muscle which is consistent with Flexor Digitorum Accessorius Longus (FDAL) muscle attaches medial plantar part of calcaneus (d, most distal image).
Multiple accessory muscles of ankle have been described in literature as mentioned previous cases. FDAL is located in the deep posterior compartment of ankle. Ankle accessory muscles are typically asymptomatic but may cause compressive neuropathy like in this case. During course of muscle, it may compress the neurovascular bundle within the tarsal tunnel and cause tarsal tunnel syndrome. It may cause also FHL tenosynovitis.
The accessory navicular bone is one of several accessory ossicles of the foot and is considered as a normal anatomic and radiographic variant. Three types of accessory navicular bone have been described. The type II accessory navicular is the most commonly symptomatic variant with localized chronic or acute on chronic medial foot pain and tenderness with associated inflammation of overlying soft tissues. Tibialis posterior tendon may attach to this accessory bone, and may cause instability of this accessory bone which is called as accessory navicular syndrome. Sometimes patients feel this accessory bone as soft tissue mass in medial side of navicular bone.
Various anatomical variations including accessory muscles-bones, coalitions, sesamoid bones can be found in ankle. These anatomical variations may cause ankle and foot problems.

0 COMMENTS
These issues are no comments yet. Write the first comment...